Another Earthquake in Haiti?
Update, August 14, 2021
A new earthquake of magnitude 7.2 at shallow depths occurred, due to oblique reverse motion along the Enriquillo-Plantain Garden fault zone. According to the USGS, the earthquake most likely resulted from a fault that struck west and dipped to the north with a component of left-lateral slip. The earthquake happened in the southern peninsula, near a small town called Saint Louis du Sud, on the southern coast, 22 miles from Cayes. It was 180 miles from Jérémie, which is quite far to the west, on the northern coast of the peninsula.
By Dady Chery
Haiti Chery
Haiti’s densely populated greater Port-au-Prince area is seismically more active than previously thought, and there will be another earthquake there. It is impossible to predict when this will happen.
A study by a team of French scientists, published in December 2015, helps to understand that some exceptional forces caused Haiti’s extremely destructive magnitude-7.0 earthquake on January 12, 2010 and that there is continuing seismic risk to the city of Port-au-Prince and its surroundings. In an article in Geophysical Research Letters, Nathalie Feuillet and her colleagues identified the faults that were involved in the earthquake, and they proposed an unusual model for the seismic rupture that well fits the available observations.
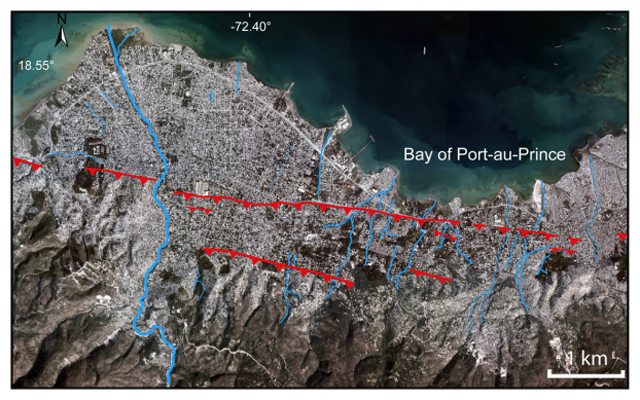
Active fault through the city of Carrefour, west of Port-au-Prince (red) (Credit: Newdeskarl Saint Fleur et al. GRL, 2016.).
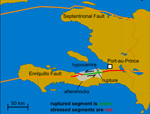
Haiti’s January 12, 2010 earthquake has been difficult to map in detail, because it left no trace of surface rupture. The general public was made to understand that stresses on the Enriquillo-Plantain Garden Fault (EPGF), a major left-lateral strike-slip through Haiti’s southern peninsula, were generally the source and location of the earthquake. To those who study seismo-tectonics, however, the epicenter of the earthquake was not adequately mapped. Typically, earthquakes along the EPGF leave offsets of several meters in the landscape. There therefore arose the notion that Haiti’s 2010 earthquake had ruptured one or more previously unmapped blind thrusts (faults that show no sign on the earth’s surface) north of the EPGF.
By combining data from aerial images, high-resolution topography, bathymetric maps (maps of the submerged terrain), and geological observations, the researchers managed to map a sizeable set of active blind thrusts running northwest through Haiti’s southern peninsula toward the bay, many of them right in the plain that includes Port-au-Prince. They singled out one of these, called the Lamentin thrust, which connects to the EPGF to the east, near Pétion-Ville, and runs northwest through the city of Carrefour and into the bay, as having been involved in the earthquake.
Based on the above physical measurements, plus maps of the aftershocks, the scientists built a model of the earthquake that fit “the surface deformations recorded by geodetic (GPS and radar interferometry) data and micro-atolls type of corals.”
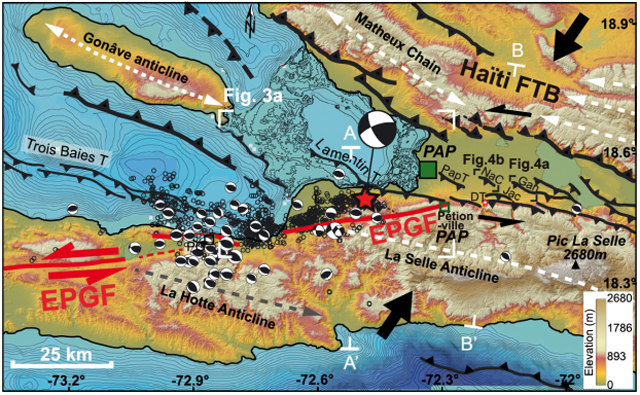
Active faults and seismicity in the southwestern part of Haiti. Red star = epicenter of the main shock of the earthquake of 2010. Blind thrusts are shown (black lines), as well as the EPGF (red line). Note the connection of the Lamentin thrust to the EPGF (Credit: Newdeskarl Saint Fleur et al GRL, 2016).
They concluded from their model that what happened in Haiti on January 12, 2010 was probably an exceptional event: a coupled rupture of two faults. In other words, there were two earthquakes in quick succession, with the first one causing the second. Specifically, both the Lamentin thrust and the EPGF, which connect at depth, were ruptured on that day, and the rupture probably started with a strong sliding along the Lamentin thrust before it spread along the EPGF. A huge drop in the perpendicular compression on the EPGF is apparently what promoted its rupture.
On one hand, Haiti’s 2010 earthquake relieved stresses that had accumulated over more than 20 decades. On the other hand, after the earthquake, the stresses increased at both ends of the rupture zone, according to the researchers. Furthermore, the presence of many active blind thrusts in the greater Port-au-Prince area could represent additional earthquake risks. Some scientists even suggest that the area’s earthquakes tend to come in series. For example, the last recorded major earthquake in Port-au-Prince, around magnitude-7.5, was in 1770, but 10 earthquakes of magnitude 6.0-6.9 preceded it, between 1765 and 1770, and there were two earthquakes of magnitude-6.5 to 6.7 in 1751 alone.
The greater Port-au-Prince area hosts about three million people. It includes, not only the capital city, but also the suburbs of Carrefour, Pétion-Ville, Delmas, Tabarre, Cité Soleil, and Kenskoff, plus the neighboring cities of Léogâne, Miragoâne, and Gressier. Therefore, it is prudent to build new structures with the area’s seismic activity in mind and generally practice earthquake preparedness.
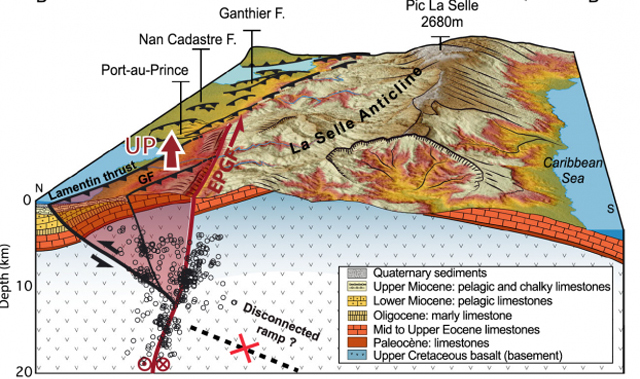
Block diagram showing a north-south cross-section of the geology and aftershocks of the main earthquake and fault system (Credit: Newdeskarl Saint Fleur et al GRL, 2016).
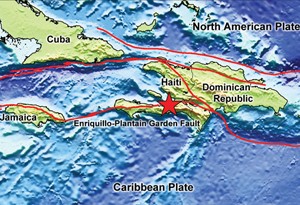
Sources: Haiti Chery | Dady Chery is the author of We Have Dared to Be Free | Actualités du CNRS-INSU “Seismotectonics of southern Haiti: A new faulting model for the 12 January 2010 M7.0 earthquake” (2015) Newdeskarl Saint Fleur, Nathalie Feuillet, Raphaël Grandin, Eric Jacquesv, Jennifer Weil-Accardo, and Yann Klinger Geophysical Research Letters – 12 December 2015 doi/10.1002/2015GL065505/ Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Université Paris Diderot, CNRS. | Featured image: The EPGF forms part of the boundary between the North American and Caribbean plates. Present-day plate boundaries (red lines), epicenter of 12 January 2010 earthquake (red star) (Credits: Lisa Gahagan/Institute for Geophysics, UTIG; Walter Smith and David Sandwell/UTIG, USGS).